Economies of scale refers to the phenomenon where the average costs per unit of output decrease with the increase in the scale or magnitude of the output being produced by a firm. External economies of scale happen because of larger changes within the industry, such as.
What Is Economies Of Scale In Simple Terms, Economies of scale are the financial advantages that a company gains when it produces. Economies of scale refer to the lowering of per unit costs as a firm grows bigger.

Economies of scale are of two types, namely internal and external economies of scale. (lower average costs) diagram economies of scale. The internal economies of scale are the internal factors that can be controlled by the organisation to lower the cost of production. Economies of scale are of two types, namely internal and external economies of scale.

When a perfectly competitive firm is in long run equilibrium It is a long term concept. Thus, it is quite possible and common to have an industry that has both diminishing marginal returns when only one input is allowed to change, and at the same time has increasing or constant economies of scale when all inputs change together to produce a larger. Economies of scale are defined as the link.

Constant returns to scale Economics Help These benefits are called as economies of scale. Internal economies of scale originate from internal factors within the organisation. Definition of economy of scale : However, economies of scale may also arise from an increase in the number of plants of a firm, irrespective of whether the firm continues to produce the same. This will happen when the organization grows.

Economies and Diseconomies of Scale 1406 Words Essay Example For certain industries, with significant economies of scale, e.g aeroplane manufacture, it is important to be a large firm; As a result, the savings of the organization increases, which further enables the organization to obtain raw materials in bulk. Economies of scale are said to be achieved when more units of a service or good can be produced on a.
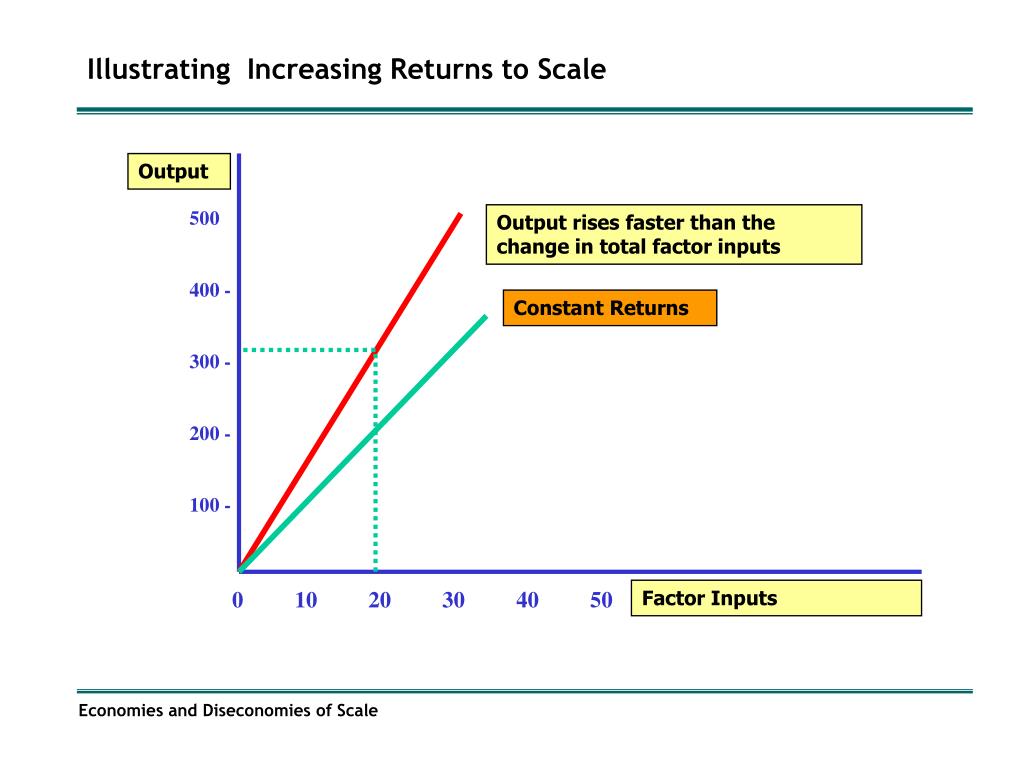
Increasing Returns To Scale Increasing returns to scale. Decreasing Similarly, the opposite phenomenon, diseconomies of scale, occurs when the average unit costs of production increase beyond a certain level of output. However, economies of scale may also arise from an increase in the number of plants of a firm, irrespective of whether the firm continues to produce the same. Internal economies of scale are particular to a certain company.

Monopolistic Competition tutor2u Economics Economies of scale are the reduction in the per unit cost of production as the volume of production increases. Economies of scale arise when unit costs fall as output rises. Economies of scale are said to be achieved when more units of a service or good can be produced on a bigger or a larger scale, that too with (on.

Economies of Scale Napkin Finance Specialization and division of labour Economies of scale are important because they mean that as firms increase in size, they can become more efficient. In this article, we will look at the internal and external, diseconomies and economies of scale. Examples of economies of scale. Second, they lower the cost per variable unit, as the larger scale makes the whole.

Financial Management Concepts in Layman�s Terms The reduction of production costs that is a result of making and selling goods in large quantities…. As a result, the savings of the organization increases, which further enables the organization to obtain raw materials in bulk. Diseconomies of scale, on the other hand, occur when the output increases to such a great extent that the cost per unit starts.

Diseconomies of Scale Chart External economies of scale happen because of larger changes within the industry, such as. This is because the fixed cost remains same irrespective of the level of. As a result, the savings of the organization increases, which further enables the organization to obtain raw materials in bulk. Economies of scale occur when increased output leads to lower unit costs. Economies.

Economies of Scale YouTube Examples of economies of scale. For certain industries, with significant economies of scale, e.g aeroplane manufacture, it is important to be a large firm; Examples of economies of scale include: On the other hand, external economies of scale are the external factors. Specialization and division of labour

Internal Economies of Scale Economics tutor2u A company would have achieved economies of scale when the cost per unit reduces as a result of an expansion in the firm’s operations. Economies of scale are the reduction in the per unit cost of production as the volume of production increases. Examples of economies of scale. At the basis of economies of scale there may be technical, statistical,.

6.2 External Economies of Scale YouTube In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced. Otherwise they will be inefficient. Similarly, the opposite phenomenon, diseconomies of scale, occurs when the average unit costs of production increase beyond a certain level of output. Examples of economies of scale.

What is Economies of Scale? Napkin Finance has the answer for you! The internal economies of scale are the internal factors that can be controlled by the organisation to lower the cost of production. A company would have achieved economies of scale when the cost per unit reduces as a result of an expansion in the firm’s operations. Economies of scale are of two types, namely internal and external economies of scale..

Perfect Competition Adjusting to Long Run… tutor2u Economics Economies of scale are the financial advantages that a company gains when it produces. On the other hand, external economies of scale are the external factors. Economies of scale occurs when more units of a good or service can be produced on a larger scale with (on average) fewer input costs. Economies of scale are said to be achieved when.

Distinguish Between Diminishing Returns and Economies of Scale | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples Diseconomies of scale, on the other hand, occur when the output increases to such a great extent that the cost per unit starts increasing. This is because the fixed cost remains same irrespective of the level of. Economies of scale are important because they mean that as firms increase in size, they can become.

Economies of Scale Definition, Types, Internal, External At the basis of economies of scale there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control. Economies of scale are of two types, namely internal and external economies of scale. Economies of scale are said to be achieved when more units of a service or good can be produced on a bigger or a.

Profit Maximization and Increasing Returns to Scale Marketplace Economics Economics of scale depends more on the production capacity of one product. A reduction in the cost of producing something (such as a car or a unit of electricity) brought about especially by increased. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. Economies of scale are the reduction in the per unit cost of production.

Economies of Scale vs Economies of Scope Top Differences You Must Economies of scope concentrate on varieties of products. Similarly, the opposite phenomenon, diseconomies of scale, occurs when the average unit costs of production increase beyond a certain level of output. However, economies of scale may also arise from an increase in the number of plants of a firm, irrespective of whether the firm continues to produce the same. In other.

CMA Economics 14 Theory of Production Law of Variable Proportion Law A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. There are two primary types of economies of scale: In this article, we will look at the internal and external, diseconomies and economies of scale. | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples (lower average costs) diagram economies of scale.

Factors Influencing Global Economy Management Guru Management Guru Second, they lower the cost per variable unit, as the larger scale makes the whole system of production more systematic and efficient. Economies of scale is a concept that is widely used in the study of economics and explains the reductions in cost that a firm experiences as the scale of operations increase. On the other hand, external economies of.
![]()
Economic Terms Glossary EzyEducation Economies of scale are the reduction in the per unit cost of production as the volume of production increases. This is because the fixed cost remains same irrespective of the level of. Second, they lower the cost per variable unit, as the larger scale makes the whole system of production more systematic and efficient. A reduction in the cost of.

Elasticity Level 3 Economics Human Capital Pro Economies of scale refers to the phenomenon where the average costs per unit of output decrease with the increase in the scale or magnitude of the output being produced by a firm. Economies of scale are of two types, namely internal and external economies of scale. Last updated 30 oct 2018. Economies of scale is a concept that is widely.

Economies of Scale Explained In Simple Terms YouTube Economies of scale occurs when more units of a good or service can be produced on a larger scale with (on average) fewer input costs. This diagram shows that as firms increase output from q1 to q2, average costs fall from p1 to p2. The reduction of production costs that is a result of making and selling goods in large.

Economies of scale CEOpedia Management online This helps the organization to enjoy discounts. Otherwise they will be inefficient. Economies of scale is a concept that is widely used in the study of economics and explains the reductions in cost that a firm experiences as the scale of operations increase. Economies of scale refer to the lowering of per unit costs as a firm grows bigger. There.

Increasing Returns To Scale Increasing returns to scale. Decreasing This is because the fixed cost remains same irrespective of the level of. It is a long term concept. Last updated 30 oct 2018. First, economies of scale reduce the fixed cost for each unit produced, because higher production levels mean fixed costs are distributed over a greater number of total units. In this article, we will look at the.

Economies of Scale and Scope in Banking Industry However, economies of scale may also arise from an increase in the number of plants of a firm, irrespective of whether the firm continues to produce the same. Economies of scale (with diagram) economies which arise from the firm increasing its plant size. Last updated 30 oct 2018. This is because the fixed cost remains same irrespective of the level.
A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. Economies of Scale and Scope in Banking Industry.
These benefits are called as economies of scale. Definition of economy of scale : Internal economies of scale originate from internal factors within the organisation. Economies of scale refer to the lowering of per unit costs as a firm grows bigger. A company would have achieved economies of scale when the cost per unit reduces as a result of an expansion in the firm’s operations. Similarly, the opposite phenomenon, diseconomies of scale, occurs when the average unit costs of production increase beyond a certain level of output.
For certain industries, with significant economies of scale, e.g aeroplane manufacture, it is important to be a large firm; This is because the fixed cost remains same irrespective of the level of. By the term economies of scale, we mean the increase in the efficiency of production due to the increase in size, output or activity level. Economies of Scale and Scope in Banking Industry, It is a long term concept.







