This curve is called the learning curve. Learning curves don’t only apply to learning a new job, though.
Learning Curves Explained, A learning curve is a concept used to measure how quickly a skill can be mastered. A good way to check whether the model is overfitting or underfitting is to generate learning curves.

It depicts how a boost in learning happens because of greater experience. Made a video on learning curves. This curve is called the learning curve. We’re going to start with a simple linear regression model and improve it as much as we.

Nov 2015 Teaching Tip » The initial stage in the above curve is that of slow learning because of the newness and difficulty of skill. We thus have two error scores to monitor: Explore the meaning of “learning curve” idiomatic expression with examples and origin details. As you begin to understand learning curves, consider the two different learning curve models. A learning curve is a.

AUCROC Curve Visually Explained Learn Machine Learning One for the validation set, and one for the training sets. Learning curves are a widely used diagnostic tool in machine learning for algorithms that learn from a training dataset incrementally. The learning curve is the tendency for beginners in a subject or domain to learn slowly but to gain in learning efficiency over time. Changes are made in the.
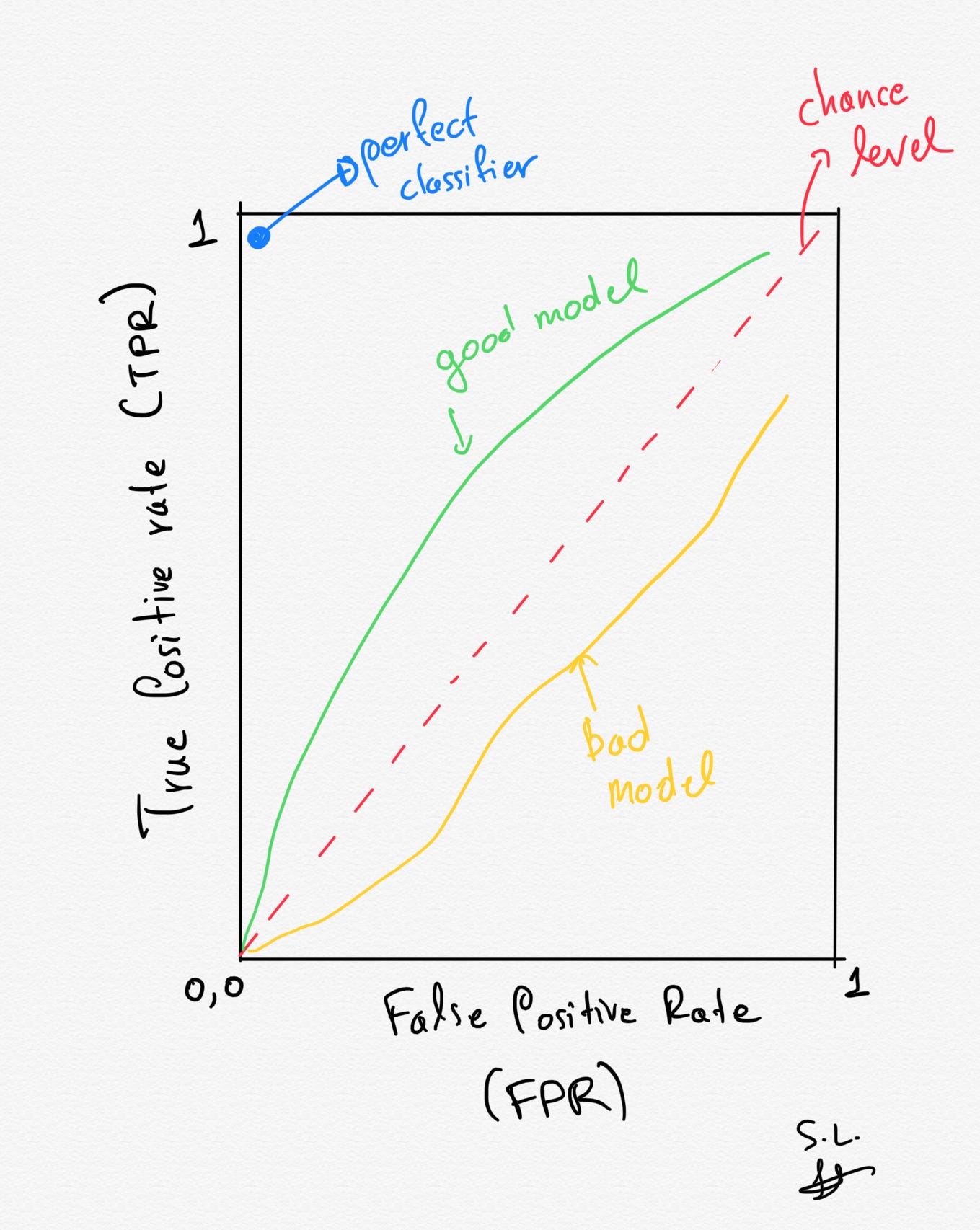
ROC Curve explained using a COVID19 hypothetical example Binary A learning curve is just a plot showing the progress over the experience of a specific metric related to learning during the training of a machine learning. Y = the cumulative average time (or cost) per unit. The learning curve is another great tool to have in any data scientist’s toolbox. The initial stage in the above curve is that.

HBR Throw Your Life an SCurve Whitney Johnson Hopefully, you guys like it. X = the cumulative number of units produced. Learning curves are often used to measure an individual’s progress against an average. A learning curve is a concept used to measure how quickly a skill can be mastered. This curve is very important in cost analysis, cost estimation and efficiency studies.

AUCROC Curve Visually Explained Learn Machine Learning Accumulative average time per unit The learning curve (not to be confused with experience curve) is a graphical representation of the phenomenon explained by theodore p. Once the learner has acquired some basics of his. The learning curve shows that if a task is performed over and over than less time will be required at each iteration. The learning curve.

AUCROC Curve Visually Explained Learn Machine Learning A learning curve is a visual representation of the change in production efficiency over time. It requires lots of “babysitting”; A learning curve is just a plot showing the progress over the experience of a specific metric related to learning during the training of a machine learning. Usually shown as a simple graph, it often depicts the combination of the.

The MacLeamy curve Daniel Davis The learning curve shows that if a task is performed over and over than less time will be required at each iteration. It refers to the effect that learning had on labour productivity in the aircraft industry, which translates into a relation between the cumulative number of units produced (x) and the. A learning curve is just a plot showing.

What Is The Experience Curve And Why It Matters In Business FourWeekMBA Wright in his “factors affecting the cost of airplanes”, 1936. Please share any feedback you might have. There are substantial and varying differences in rates of production. There are three major assumptions in the learning curve effect: Learning curve function is defined as follows:

Learning Curve Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Computer Vision Usually shown as a simple graph, it often depicts the combination of the time it takes to learn a new idea or skill set, combined with the rate at which mastery is achieved. What is the formula of learning curve?? Learning curve in machine learning is used to assess how models will perform with varying numbers of training samples. Once.

Learning curves for perceptron learning algorithm with = 04 and = 06 It refers to the effect that learning had on labour productivity in the aircraft industry, which translates into a relation between the cumulative number of units produced (x) and the. It depicts how a boost in learning happens because of greater experience. Made a video on learning curves. Y = the cumulative average time (or cost) per unit. We have.

What is The Learning Curve Explained in 2 min YouTube Wright in his “factors affecting the cost of airplanes”, 1936. If we plot the evolution of the two error scores as training sets change, we end up with two curves. There are substantial and varying differences in rates of production. Learning efficiency increases as you gain experience and then plateaus at a point where you can understand new information in.
![ROCAUC curve explanation [30]. Download Scientific Diagram ROCAUC curve explanation [30]. Download Scientific Diagram](https://i2.wp.com/www.researchgate.net/publication/340509015/figure/download/fig3/AS:878058684809231@1586356912709/ROC-AUC-curve-explanation-30.png)
ROCAUC curve explanation [30]. Download Scientific Diagram In a nutshell, a learning curve shows how error changes as the training set size increases. The learning curve is the tendency for beginners in a subject or domain to learn slowly but to gain in learning efficiency over time. The initial stage in the above curve is that of slow learning because of the newness and difficulty of skill..

The Explanation Age Nextgeneration Thought Leadership Coaching Explained and a graphic from: These are called learning curves. The learning curve is another great tool to have in any data scientist’s toolbox. Learning efficiency increases as you gain experience and then plateaus at a point where you can understand new information in a domain quickly. Learning curves are often used to measure an individual’s progress against an average.

Learning curves of the PFLD for various feature sizes. Download A good way to check whether the model is overfitting or underfitting is to generate learning curves. Once the learner has acquired some basics of his. The steeper the slope, the higher the cost savings per unit of output. Proficiency (measured on the vertical axis) usually increases with increased experience (the horizontal axis), that is to say, the more someone.

ROC Curve & AUC Explained with Python Examples Data Analytics As you begin to understand learning curves, consider the two different learning curve models. A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how proficient someone is at a task and the amount of experience they have. Learning curves exist because as individuals and teams repeatedly perform the same tasks their efficiency at them increases, reducing the time.
![]()
Learning curve Policonomics = log of the learning rate/log of2. Learning curve function is defined as follows: It shows the relationship between the training score and the test score for a machine learning model with a varying number of training samples. Accumulative average time per unit Explore the meaning of “learning curve” idiomatic expression with examples and origin details.

32 Refer To The Diagram To The Right. Identify The Curves In The Monitoring, data preparation, and experimentation, especially if it’s a new project. New employees learn faster than old ones. This includes some of my work experience, as well as other things. A = time (or cost) required to produce the first unit. Such effect of increased efficiency with production volume is known as the ‘learning curve’ effect.

Entry 30 Improve Performance Learning Curves Data Science Diaries It depicts how a boost in learning happens because of greater experience. Explained and a graphic from: There are three major assumptions in the learning curve effect: Changes are made in the normal size of the production run. What is the formula of learning curve??

r How to determine how much of the variation in a binary dependent Learning curve shows the relationship between the time spend on doing the same tasks and the improvement. It refers to the effect that learning had on labour productivity in the aircraft industry, which translates into a relation between the cumulative number of units produced (x) and the. These are plots of the model’s performance on the training set and the.
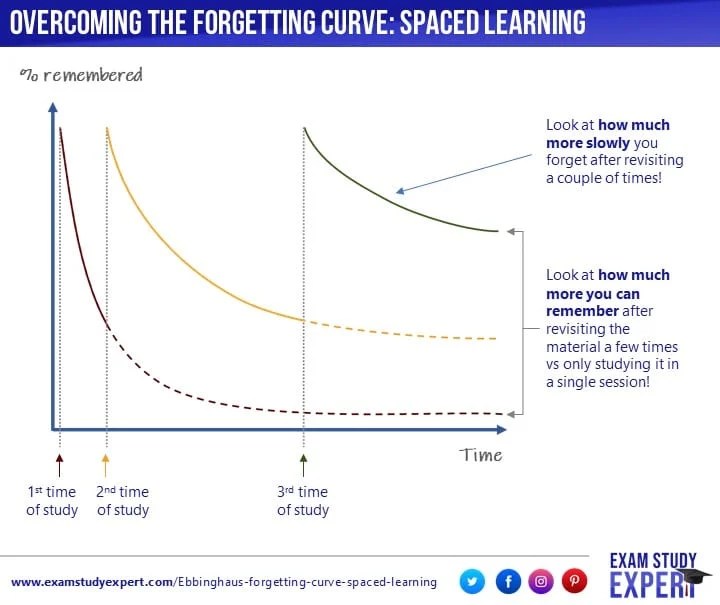
Ebbinghaus� Curve Explained The Importance Of Spaced = log of the learning rate/log of2. The difference between accept and except explained with examples. The learning curve provides insight into productivity, efficiency, cost, and experience. Thus it is also known by the names of productivity curve, efficiency curve, cost curves, and. The steeper the slope, the higher the cost savings per unit of output.

Spark MLlib Tutorial In a nutshell, a learning curve shows how error changes as the training set size increases. In all that process, learning curves play a fundamental role. These are plots of the model’s performance on the training set and the validation set as a function of the training set size. In management accounting, we expect that the worker will spend less.

The Manifesting Learning Curve Good Vibe Blog Explained and a graphic from: Improvement in the direct labour functions reduces the direct labour content in the product. Learning curves are useful in analyzing a machine learning model’s performance over various sample sizes of the training dataset. Usually shown as a simple graph, it often depicts the combination of the time it takes to learn a new idea or.

Learning curves of the PFLD for various feature sizes. Download These are plots of the model’s performance on the training set and the validation set as a function of the training set size. There are substantial and varying differences in rates of production. Wright in his “factors affecting the cost of airplanes”, 1936. We’re going to start with a simple linear regression model and improve it as much as we..

Top 3 websites for Lighting TDs renderstory The learning curve provides insight into productivity, efficiency, cost, and experience. Improvement in the direct labour functions reduces the direct labour content in the product. A learning curve is a concept used to measure how quickly a skill can be mastered. Y = the cumulative average time (or cost) per unit. It depicts how a boost in learning happens because.

What you need to know… about The Curve of Proficiency (measured on the vertical axis) usually increases with increased experience (the horizontal axis), that is to say, the more someone performs a task, the better their performance at. This includes some of my work experience, as well as other things. The steeper the slope, the higher the cost savings per unit of output. The basic theory behind the concept.
Learning curves are often used to measure an individual’s progress against an average. What you need to know… about The Curve of.
A learning curve is a visual representation of the change in production efficiency over time. A learning curve is a concept used to measure how quickly a skill can be mastered. Please share any feedback you might have. Learning efficiency increases as you gain experience and then plateaus at a point where you can understand new information in a domain quickly. A learning curve is just a plot showing the progress over the experience of a specific metric related to learning during the training of a machine learning. Learning curve in machine learning is used to assess how models will perform with varying numbers of training samples.
Learning curves are a great tool to employ if you want to set labor standards, evaluate employee performance, prepare cost estimates, and set incentive wage rates. The learning curve (not to be confused with experience curve) is a graphical representation of the phenomenon explained by theodore p. = log of the learning rate/log of2. What you need to know… about The Curve of, Learning curve of a good fit model has a high validation loss at the beginning which gradually decreases upon adding training examples and flattens gradually, indicating addition of more training examples doesn’t improve the model performance on unseen data.







