A adalah waktu yang dibutuhkan untuk menyelesaikan tugas pertama kali. The worker needs to spend 10 hours per unit during the trial period.
Learning Curve Theory Formula, The learning curve effect can be calculated by: However, the cost of each nth unit parallels the average cost after 20 or so units.

In all productive processes, there is consistent improvement in worker performance, as the process is repeated multiple times. Quick calculations provided for either a specific unit, or lot of items, given one point of historical information (it need not be the value of the first unit, a or t1, value) and the notional percentage curve under either a unit (boeing, stanford, crawford) or cumulative average (northrup, wright) formulation convention. In this section we try to model the learning process using a differential equation. This chapter introduces the concept of learning curves and explains unit theory principles in great detail.

The Learning Curve However, the cost of each nth unit parallels the average cost after 20 or so units. Secara matematika, learning curve digambarkan dengan persamaan berikut. Unit cost is reduced by “x”% every time cumulative units produced doubles: Here we know the learning curve formula is y=ax^b and b is the index of learning which can be calculated using log tables. B.

Learning Curve Theory Meaning, Formulas, Graphs Unit cost is reduced by “x”% every time cumulative units produced doubles: First of all, we introduce a measurable learning function l (t). Y = a x b where: A learning curve is a graph or equation that express the rate of improvement in productivity as more units are produced. B = log of 80%/log of.

The Curve Of Learning Learning Curve Theory Meaning Formulas Graphs A = time (or cost) taken for the first unit or batch. A = time (or cost) required to produce the first unit. The common expression a steep learning curve is a misnomer. B = log of 80%/log of. The variable y is the average time per unit of output.
![]()
Learning curve Policonomics The learning curve is based on the theory that individuals require time to become proficient at something new. A = time (or cost) required to produce the first unit. A learning curve is a graph or equation that express the rate of improvement in productivity as more units are produced. Management accounting and decisions ii. Y = cumulative average time.

Learning Curve Theory Meaning, Formulas, Graphs For a business, this means that investment needs to be made in order to obtain a certain output. X = the cumulative units of production or, if in batches, the cumulative number of batches. The common expression a steep learning curve is a misnomer. Mastering a new area or a skill always takes some time. X adalah jumlah percobaan atau.

What is a Learning Curve? X adalah jumlah percobaan atau unit keluaran. Learning curve formula y = ax b. However, the cost of each nth unit parallels the average cost after 20 or so units. The common expression a steep learning curve is a misnomer. Reducing cumulative average time by the learning rate each time output doubles in a table:

memory How are these curve calculated? Cognitive As output increases, it becomes harder and harder to. Learning curve analysis is developed as a tool to estimate the recurring costs in an assembly or production process. =$f$24*($f$3)^(ln(e25)/ln(2)) this formula can described as: The theory behind the curve. A = time (or cost) required to produce the first unit.

Learning Curve Theory Meaning, Formulas, Graphs The result is that estimates based on these texts overstate project time requirements by as much as 30%! A adalah waktu yang dibutuhkan untuk menyelesaikan tugas pertama kali. The variable y is the average time per unit of output. A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how proficient someone is at a task and the amount.

Threeparameter exponential learning curve by learning rate. Download B represents the slope of the function. The learning curve, expressed as an algebraic formula, is as follows: Learning curve formula y = ax b. The theory behind the curve. For an 80% learning curve b = log.8/log 2 =.

Typical Learning Curve for Newly Learned Information « Mind Bursts The learning curve effect can be calculated by: B = log of 80%/log of. Secara matematika, learning curve digambarkan dengan persamaan berikut. P = the learning percentage A = time (or cost) required to produce the first unit.

ACCA PM (F5) Notes D2bc. Learning effect and Learning Curve X is the total number of attempts or units of output. This means that variable cost per unit an d fixed costs remain unchanged. A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how proficient someone is at a task and the amount of experience they have. When a learning curve initially ascends steeply, this means. A is.
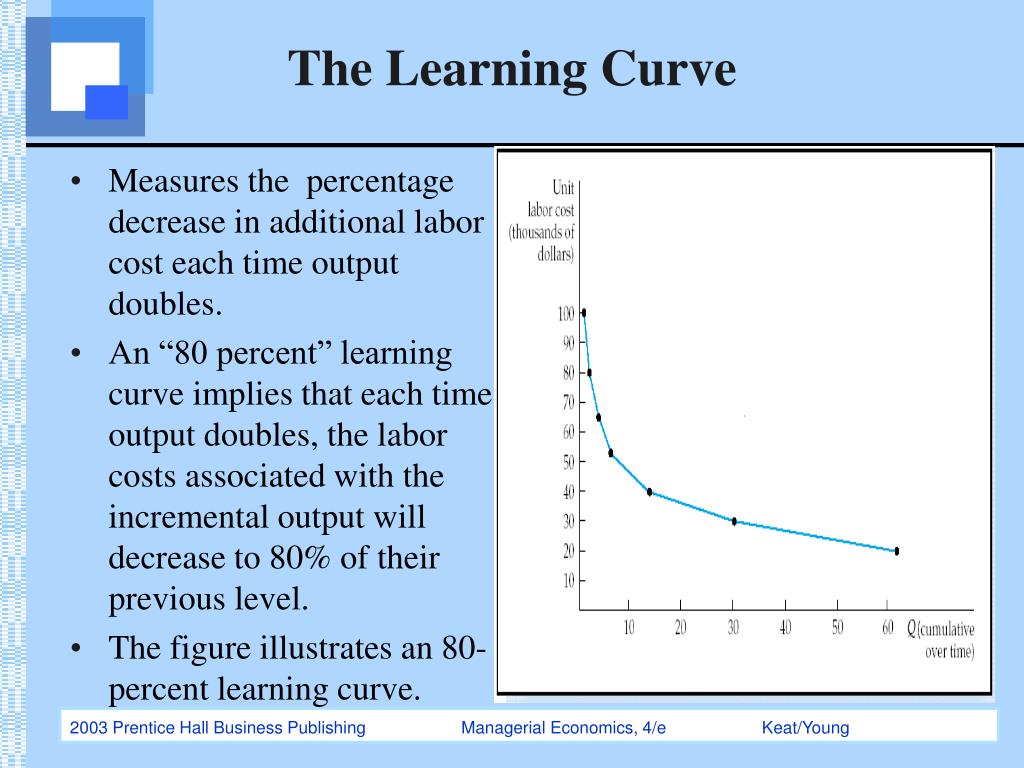
PPT The Theory and Estimation of Cost PowerPoint Presentation, free In this excel file i converted the formal equation into a formula: Management accounting and decisions ii. Accumulative average time per unit. Index of learning, [b= log (learning curve percentage) ÷ log 2] example. However, the cost of each nth unit parallels the average cost after 20 or so units.

Learning Curve Theory Meaning, Formulas, Graphs X is the total number of attempts or units of output. Accumulative average time per unit. Over time, the individual will learn and become more efficient at that task. The worker needs to spend 10 hours per unit during the trial period. This chapter introduces the concept of learning curves and explains unit theory principles in great detail.

The Truth about Learning Curves « Project Excellence for Challenging Times The concept also applies to when a person is tasked with absorbing a large amount of information. Learning curve function is defined as follows: How to use the learning curve formula. The learning curve effect can be calculated by: B = log of 80%/log of.

The Curve Of Learning Learning Curve Theory Meaning Formulas Graphs In this excel file i converted the formal equation into a formula: A = time (or cost) required to produce the first unit. And the total hours are 60 x 90 = 5449 hours. The variable y is the average time per unit of output. Management accounting and decisions ii.
Learning curve When a learning curve initially ascends steeply, this means. Reducing cumulative average time by the learning rate each time output doubles in a table: =$f$24*($f$3)^(ln(e25)/ln(2)) this formula can described as: Learning curve formula y = ax b. The theory behind the curve.

2 Scurve as model of language change Download Scientific Diagram N = theoretical first unit (tfu) x unit. A learning curve is a graph or equation that express the rate of improvement in productivity as more units are produced. However, the cost of each nth unit parallels the average cost after 20 or so units. A = time (or cost) required to produce the first unit. This function, for example,.

Learning Curve Theory Meaning, Formulas, Graphs And the total hours are 60 x 90 = 5449 hours. Y = a x b where: N = theoretical first unit (tfu) x unit. Accumulative average time per unit. X = the cumulative number of units produced.

The Learning Curve An interactive start to learning about Calculus, the How to use the learning curve formula. =$f$24*($f$3)^(ln(e25)/ln(2)) this formula can described as: Time spend for the first unit. Y = cumulative average time per unit or batch. Management accounting and decisions ii.

Area under Learning Curve (AULC) of various BMAL methods on MIRFLICKR Over time, the individual will learn and become more efficient at that task. Reducing cumulative average time by the learning rate each time output doubles in a table: = unit time hours *(learning curve percent) ^(ln(unit value)/ln(2)) unit time hours total hours to complete the first unit. Learning curve formula y = ax b. A learning curve is a graph.

Learning Curve Theory The Definitive Guide The equations associated with each model are similar. The theory behind the curve. Reducing cumulative average time by the learning rate each time output doubles in a table: B represents the slope of the function. = unit time hours *(learning curve percent) ^(ln(unit value)/ln(2)) unit time hours total hours to complete the first unit.
![]()
Experience curve Policonomics Reducing cumulative average time by the learning rate each time output doubles in a table: It shows that for every doubling of a company�s output, the cost of the new output is 80% of the prior output. Reducing cumulative average time by the learning rate each time output doubles in a table: For a business, this means that investment needs.

Learning Curve Theory Meaning, Formulas, Graphs Learning curve function is defined as follows: The learning curve effect can be calculated by: As output increases, it becomes harder and harder to. A = time (or cost) required to produce the first unit. Reducing cumulative average time by the learning rate each time output doubles in a table:

What is The Learning Curve Explained in 2 min YouTube Mastering a new area or a skill always takes some time. The worker needs to spend 10 hours per unit during the trial period. Company a manufactures product x. Formula dan cara menggunakan learning curve 1. Learning curve percent or the improvement rate.

The curve explains why humans struggle to memorize — Quartz When a learning curve initially ascends steeply, this means. The learning curve effect can be calculated by: A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how proficient someone is at a task and the amount of experience they have. And the total hours are 60 x 90 = 5449 hours. = log of the learning rate/log of2.
Over time, the individual will learn and become more efficient at that task. The curve explains why humans struggle to memorize — Quartz.
A is the time it took to complete the task the first time. P = the learning percentage And the total hours are 60 x 90 = 5449 hours. Y = the cumulative average time (or cost) per unit. Over time, the individual will learn and become more efficient at that task. Y = cumulative average time per unit or batch.
The improvement, though, goes changing, as it is sharper at the beginning, but. A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how proficient someone is at a task and the amount of experience they have. =$f$24*($f$3)^(ln(e25)/ln(2)) this formula can described as: *The curve explains why humans struggle to memorize — Quartz*, B = log of 80%/log of.







